Introduction
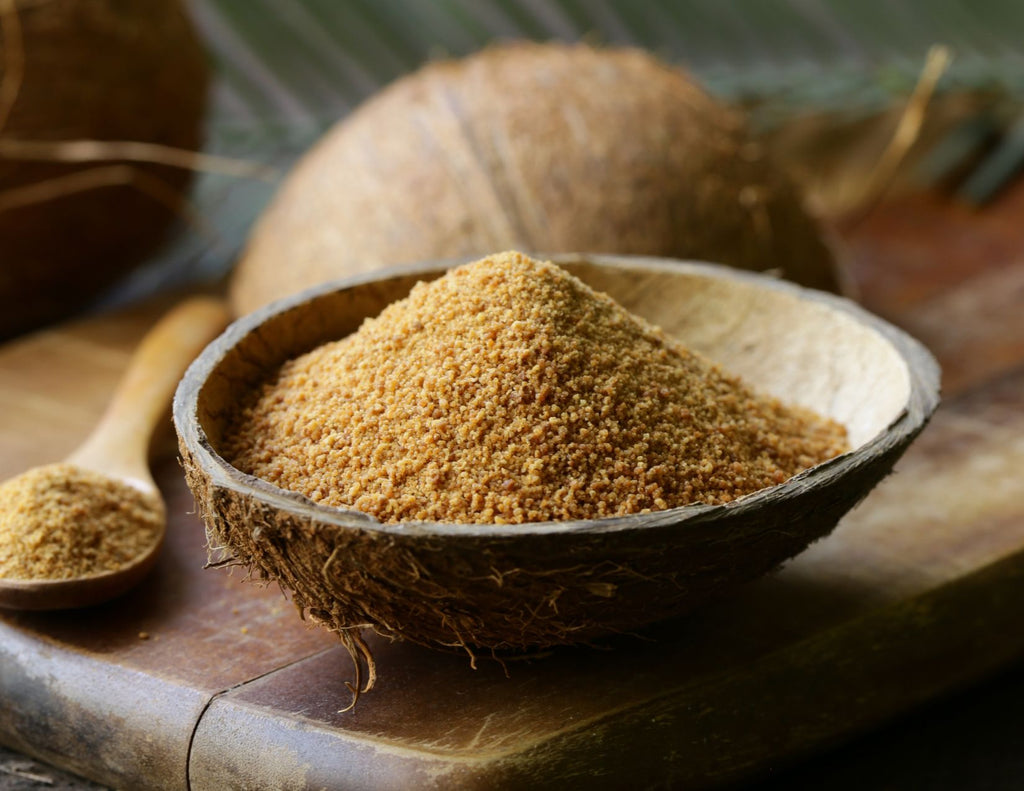
Are you looking for a sustainable alternative to traditional sugar? Look no further than coconut sugar! Not only is coconut sugar a delicious and natural sweetener, but it also has numerous benefits for both your health and the environment. Unlike traditional sugar, which is often heavily processed and bleached, coconut sugar is minimally processed and retains many of its natural nutrients. Additionally, coconut sugar has a lower glycemic index than traditional sugar, meaning it won't cause the same spikes in blood sugar levels. But the benefits of coconut sugar don't stop there. Coconut sugar is also a more sustainable option than traditional sugar, as it requires less water and energy to produce. Plus, coconut trees are highly productive and can produce up to 75% more sugar per acre than traditional sugar cane. So, if you're looking for a sweet and sustainable alternative to traditional sugar, read on to learn more about the benefits of coconut sugar!

Coconut Palms: The ‘Tree of Life’
Coconuts have been around for thousands of years and their origins are not entirely certain. The coconut is believed to have originated in the Indo-Pacific region, specifically in the areas that are now known as the Philippines and Malaysia. From there, it spread to other parts of the world, including Africa, South America, and the Caribbean. Today, coconuts are grown in over 70 countries around the world.
Coconuts are the seeds, or fruit, of the coconut palm tree, one of the most useful trees in the world. Every part of the tree can be used in one way or another, from the leaves to the roots. It’s also the only member of the palm family to produce edible fruit. The versatility of the coconut tree has earned it the name the ‘Tree of Life’ in many of these tropical regions of the world. The coconut played a significant role in regional cultures and economies, and it continues to be an important renewable resource as well as an excellent and delicious source of food.
In many island cultures, the coconut is considered a symbol of fertility and prosperity, and is used in religious ceremonies and rituals. In Hinduism, the coconut is an essential offering in numerous rituals. In some cultures, coconuts were thought to have magical properties and were used in spells and charms. In others, coconuts were believed to represent the human head, an association that springs from the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features. However, in many Polynesian cultures, these features are believed to resemble that of an eel, the form a god took to observe the beauty of a young woman.
Materially, coconuts have been used in a variety of ways. The versatile husks, which are composed of fibers, are used for objects like ropes, mats, clothing, and brushes. The shells are used as bowls and cups, and the fiber has been used for clothing and rope. The meat and milk of the coconut have been used in many different culinary dishes, and the oil has been used in traditional medicine.
Coconut sugar has been used for centuries in Southeast Asia, where coconut trees grow abundantly. It was originally used as a natural sweetener for traditional dishes and beverages. In the Philippines, it is known as "palm sugar" and is used in many desserts and snacks. In Indonesia, it is called "gula merah" and is used in various savory dishes. The historical use of coconut sugar is a testament to its versatility and importance in local cuisines.

Sustainable Production of Coconut Sugar
Historical methods of coconut cultivation involved planting the coconuts in well-drained soil and providing ample sunlight and water. Trees were often planted in groups or rows and required regular maintenance such as pruning and fertilization. In some areas, coconut cultivation involved harvesting the coconuts directly from the trees, at times employing specialized climbing equipment. Traditional methods of processing the coconuts after harvesting included drying, dehusking, and cracking the shells to extract the copra or meat inside. These methods were used for centuries before modern technology and machinery revolutionized coconut cultivation and processing.
Modern methods of coconut cultivation incorporate advanced technology and machinery, significantly improving efficiency and reducing manual labor. Mechanized systems are employed for tasks like dehusking, drying, and extracting the copra, resulting in higher yields and more consistent quality. Additionally, contemporary cultivation practices prioritize sustainability, such as organic fertilizers and integrated pest management, to minimize environmental impact. These advancements in coconut cultivation methods have increased productivity while simultaneously ensuring the long-term viability of the industry and the surrounding environment.
As a result of these practices, coconut sugar is considered to be a sustainable alternative to traditional sugar because coconut palms require less water and pesticides than sugarcane plants. Furthermore, coconut palms can produce coconut sugar for up to 20 years, while sugarcane plants need to be replanted every year. Additionally, it is worth noting that coconut sugar is traditionally produced by small farmers, and the palm trees grow organically in mixed cultivation with further crops. It provides them with a valuable source of income.

The production of coconut sugar has been a sustainable practice for generations. The production process of coconut sugar typically involves two main steps. First, the flower bud stem of a coconut tree is harvested or "tapped". A cut is made on the spadix, and the sap starts to flow from the cut into bamboo containers. Farmers collect the sap from coconut trees without harming the tree and transport it to a central processing unit, where it is heated and the water is evaporated until the sap thickens and darkens into a caramel-like consistency. The sap is then further cooked and ground, and the resulting coconut sugar is oven-dried to a moisture content of 2.5-3%. This process requires minimal energy and resources, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional sugar production.

By choosing coconut sugar, we can continue to support this sustainable practice and enjoy the delicious taste of a sweetener that has been used for centuries. That’s why it’s important to consider the ethical implications of the production and sourcing processes. There are concerns regarding the use of child labor and fair compensation for farmers. Some companies may engage in exploitative labor practices or contribute to deforestation in their production methods. Researching suppliers that prioritize fair labor practices and sustainable agriculture can help. Additionally, purchasing from certified organic and fair trade sources can help ensure ethical considerations are being met. Throughout history, coconuts have provided various foods and products that serve as integral staples for countless populations. Supporting ethical and sustainable practices helps to secure the continued vitality of this resource.

The Nutritional Benefits of Coconut Sugar
Coconut sugar undergoes very little processing, allowing it to retain some of its natural vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Coconut sugar is rich in potassium, magnesium, zinc, and iron, all of which are important for maintaining good health. It also contains antioxidants, which can help protect your body against free radical damage and reduce inflammation.
Coconut sugar may have some other potential health benefits, such as managing diabetes, boosting the immune system, strengthening bones, reducing weight gain, and improving mood. Unlike other common sweeteners like refined sugar and high fructose corn syrup, coconut sugar is low glycemic, meaning it doesn't cause a spike in blood sugar levels. This is due to a soluble fiber called inulin, which not only doesn’t cause blood sugar spikes, but is also great for gut health. This makes coconut sugar a great alternative for those with diabetes or those looking to manage their sugar intake. However, like any sweetener, it should still be consumed in moderation, as it is still a source of added sugars.
Conclusion
So the next time you’re looking to satisfy a craving for something sweet, why not try coconut sugar as a healthy and sustainable alternative to traditional sugar? It has a delicious caramel-like flavor that can be used in a variety of recipes, from baked goods to coffee and tea. Not only does it have a lower glycemic index, but it also contains essential vitamins and minerals. Additionally, the process of harvesting and producing coconut sugar is environmentally friendly and supports local communities. By choosing coconut sugar over traditional sugar, we can make a positive impact on our health and the planet. It's time to ditch the processed sugar and opt for a sweetener that not only tastes great but also benefits our bodies and the environment. Let's make a conscious effort to support sustainable practices and make a difference in the world, one sweetener at a time.
Sources
Yeyen Maryani et al. Identification of Macro Elements (Sucrose, Glucose and Fructose) and Micro Elements (Metal Minerals) in the Products of Palm Sugar, Coconut Sugar and Sugar Cane. Joint proceedings of the 2nd and the 3rd International Conference on Food Security Innovation (ICFSI 2018-2019) Advances in Biological Sciences Research, 2021. DOI 10.2991/absr.k.210304.051
Saraiva, Ariana, Conrado Carrascosa, Fernando Ramos, Dele Raheem, Maria Lopes, and António Raposo. 2023. "Coconut Sugar: Chemical Analysis and Nutritional Profile; Health Impacts; Safety and Quality Control; Food Industry Applications" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043671
Coconut Sugar: Benefits, Side Effects, and How to Make It, https://www.doctorshealthpress.com/coconut-sugar-benefits-side-effects/
11 Amazing Coconut Sugar Benefits & Uses, https://www.organicfacts.net/coconut-sugar.html
The Nutrition and Benefits of Coconut Sugar, https://www.livestrong.com/article/367337-what-are-the-benefits-of-coconut-sugar/
Coconut Sugar: Are There Health Benefits?, https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-coconut-sugar
Coconut Sugar: A Healthy Sugar Alternative or a Big, Fat Lie?, https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/coconut-sugar